Managing your router’s settings is crucial for ensuring a secure, efficient, and personalized network experience. One commonly used IP address for router configuration is 192.168.10.1. This guide walks you through everything you need to know about accessing and utilizing this IP address, from logging in to troubleshooting issues.

What is 192.168.10.1?
The IP address 192.168.10.1 is a private address commonly used as a default gateway for several routers. This address is part of the IPv4 private address space, which means it is not accessible from the internet and can only be used within a local network. Manufacturers like D-Link, Linksys, and TP-Link often designate 192.168.10.1 for their router models. By accessing this gateway, users can log in to the router’s admin console to configure network settings, update security protocols, and manage connected devices.
How to Access the Admin Panel of 192.168.10.1
Accessing your router’s admin console is the first step toward configuring your network. Here are the detailed steps:
- Connect to the Network
Ensure that your device (computer, smartphone, or tablet) is connected to the router. This can be done via Wi-Fi or an Ethernet cable. For a stable connection during setup, using an Ethernet cable is recommended. - Open a Web Browser
Launch any web browser on your device, such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Safari. - Enter the IP Address
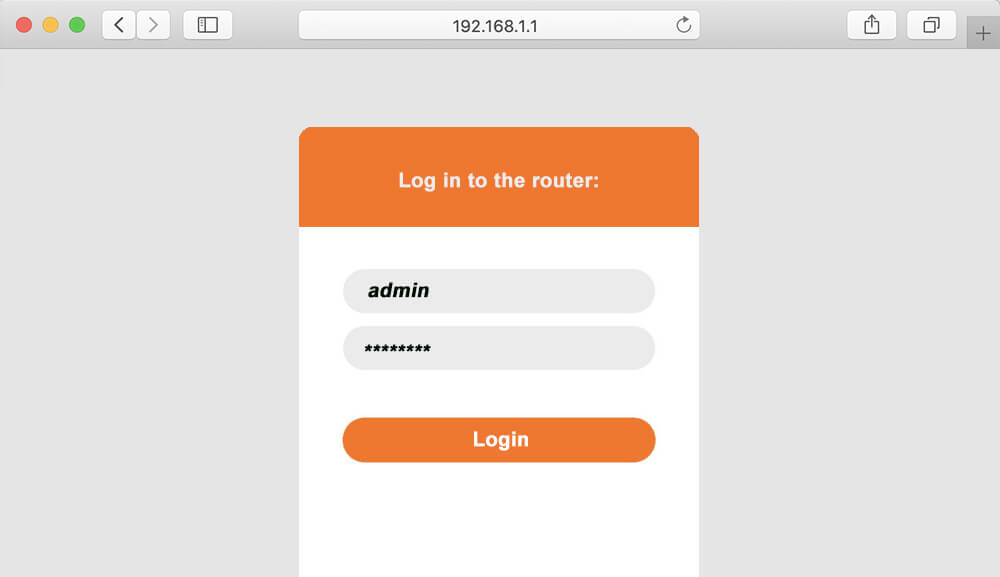
In the browser’s address bar, typehttp://192.168.10.1and press Enter. This action will direct you to the router’s login page. - Input Login Credentials
Once on the login page, enter the default username and password for your router. Common credentials include:
- Username: admin
- Password: admin, password, or 1234 These credentials may vary depending on the manufacturer. Check the router’s manual or look for a label on the device for the correct details. If the credentials have been changed and forgotten, a factory reset may be required to regain access.

Here’s an table with additional details for routers using 192.168.10.1 as the default gateway:
| Router Brand | Default Username | Default Password | Default SSID | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRENDnet | admin | admin | TRENDnet_XXXXXX | XXXXXX represents the last 6 characters of the router’s MAC address. |
| D-Link | admin | admin | D-Link_XXXX | Some models use “user” as the default username. |
| ZyXEL | admin | 1234 | ZyXEL_XXXXXX | Password may vary depending on the model. Check the router label for confirmation. |
| Cisco | admin | admin | CiscoXXXXX | Often used for business-grade routers. Some models use “cisco” as both username and password. |
| TP-Link | admin | admin | TP-LINK_XXXXXX | Default SSID and password are usually printed on the router’s label. |
| Netgear | admin | password | NETGEAR_XXXXXX | Advanced models might have separate admin credentials printed on the router. |
| Asus | admin | admin | ASUS_XXXXXX | Check the router’s sticker for a unique setup URL like http://router.asus.com. |
| Belkin | admin | admin | Belkin_XXXX | For newer models, setup may require a mobile app. |
| Huawei | admin | admin | Huawei-XXXX | Huawei routers often have a unique setup key printed on the back. |
| Linksys | admin | admin | LinksysXXXXX | Linksys Smart Wi-Fi routers require creating a user account for remote management. |
| Comtrend | root | 12345 | Comtrend_XXXX | Password is model-specific. Refer to the manual if these credentials don’t work. |
| Tenda | admin | admin | Tenda_XXXXXX | Tenda routers often use “admin” for both the username and password. |
| MikroTik | admin | (no password) | MikroTik-XXXXXX | Password is empty by default; it should be set during the initial setup for security. |
| Actiontec | admin | password | ActiontecXXXX | Often used by internet service providers (ISPs) for their router/modem combos. |
| Arris | admin | password | ARRIS-XXXX | Many Arris devices use a unique SSID and Wi-Fi key printed on a label. |
| Ubiquiti UniFi | ubnt | ubnt | UniFi-XXXXXX | Default credentials work for standalone setups but require a UniFi Controller for advanced features. |
| Motorola | admin | motorola | Motorola_XXXXXX | Often used by ISPs for modem/router combinations. |
| NetComm | admin | admin | NetCommXXXX | Ensure the router is updated with the latest firmware for optimal performance and security. |
| SMC Networks | smcadmin | smcadmin | SMC_XXXXXX | Some models may have additional security settings enabled by default. |
| Buffalo | admin | password | BuffaloXXXX | Buffalo routers support advanced features like DD-WRT firmware for customization. |
Setting Up Your Router Using 192.168.10.1
After successfully logging into the admin panel, you can customize a wide range of settings to optimize and secure your network. Here are the primary configurations to consider:
- Changing the Default Login Credentials
The default username and password are often publicly available, making your router vulnerable to unauthorized access. Navigate to the admin panel’s security settings to change these credentials to something unique and secure. Use a strong password combining uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. - Customizing the Wi-Fi Network Name (SSID)
Personalize your network by changing the SSID (Service Set Identifier). This is the name that appears when devices search for Wi-Fi networks. Go to the wireless settings in the admin panel, enter a new SSID, and save the changes. Avoid using personal information in your SSID to enhance privacy. - Setting a Strong Wi-Fi Password
Under wireless security settings, choose WPA3 or WPA2 encryption and create a robust password to protect your network from unauthorized access. - Adjusting Network Settings
Depending on your needs, you can configure advanced settings like IP address ranges, port forwarding, and Quality of Service (QoS) rules to prioritize certain types of traffic.
Troubleshooting 192.168.10.1 Connection Issues
Sometimes, accessing 192.168.10.1 might not go as smoothly as expected. Here are some troubleshooting steps to resolve common issues:
- Verify the Connection
Ensure that your device is connected to the router. If using Wi-Fi, confirm the network’s name, and for Ethernet, check that the cable is securely connected. - Confirm the IP Address
Double-check that 192.168.10.1 is the correct gateway address for your router. If unsure, refer to the router’s user manual or use system commands to verify: - On Windows: Open Command Prompt and type
ipconfig. Look for the “Default Gateway” under your network connection. - On macOS: Open Terminal and type
netstat -nr | grep default. - Clear Browser Cache
If the login page fails to load, clearing your browser cache and cookies might resolve the issue. - Restart Your Router
A simple router restart can often fix connectivity problems. Turn off the router, wait for 10 seconds, and then turn it back on. - Reset the Router
If you’ve forgotten your login credentials or made changes that prevent access, perform a factory reset. Locate the reset button (usually a small pinhole) on the router, press and hold it for about 10 seconds, and wait for the device to reboot.
Frequently Asked Questions About 192.168.10.1
What should I do if I can’t access 192.168.10.1?
Ensure your device is connected to the router’s network. If the issue persists, the router might use a different default IP address. Refer to the router manual or manufacturer’s website.
How do I find my router’s default IP address?
Use system commands like ipconfig on Windows or netstat -nr on macOS to identify the default gateway address.
What are the default login credentials for 192.168.10.1?
Common defaults include:
- Username: admin
- Password: admin, password, or 1234
How can I secure my router?
Change the default credentials, enable strong Wi-Fi encryption (WPA3 or WPA2), and regularly update the router’s firmware.
Can I use 192.168.10.1 for multiple routers?
Yes, but only within isolated networks. Each router must have a unique IP address within the same network to avoid conflicts.